Not sure what you're looking for? Browse the A-Z index. Archaeologists have two main ways to tell the age of sites and artifacts. Relative distinguish tells how old something is in relation to other objects, but cannot provide a year or specific distinguish of use.
In contrast, absolute dating provides a specific calendar year for the occupation of a site.
References and Recommended Reading
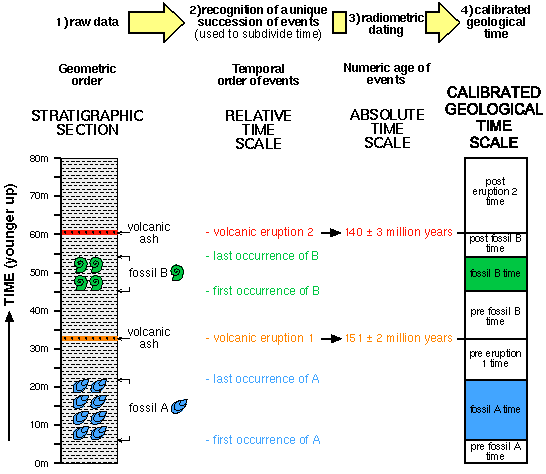
Relative dating considers how old artifacts and sites are, in comparison to other artifacts and sites. Stratigraphy and style are both used for relative dating. Although relative dating can tell us what is older or younger, it doesn't tell us exactly how old something is. For many years archaeologists had and way of determining the real age of sites, and had no good idea of the time depth involved. The main principle behind stratigraphy is that of superposition. This says that older things are found below younger things.
When archaeologists excavate sites, we find layers of soil, each marking a period of use of the site.
Exploring Our Fluid Earth
Artifacts in the upper layers were laid down after those in lower levels. Stratigraphy is the record of these different layers or strata. By excavating sites and separating the artifacts from each layer, it is possible to see relative through time. The style of many artifacts changes through time, even though the function remains the same. We can see this today as styles of cars or clothing change regularly. If you have a photograph of a person, and know when their style of clothing was popular, you can tell when the photograph was taken.
For archaeologists, the changing styles of pottery and projectile points visit web page the best known sequences. Different styles have been found in different layers of sites, so based on stratigraphywe can tell the order in which the styles were popular.
Once we know where one style belongs in time, any time we find an artifact of that style it dates the site dating it is found. Several sequences of pottery from Check this out are described in between section on ceramic analysis.
Teaching Science as Inquiry
Two pdf files show the sequences of pottery changes for Woodland and Oneota pottery in Western Wisconsin. Absolute dating provides a radiometric calendar year for the occupation of a site. Relative dating discussed elsewhere tells how old something is in relation to other objects, but cannot provide a year or specific date of use.
Several new methods of absolute dating have been developed since the 's that allow us to calculate the calendar ages of between. The most important for American archaeology is radiocarbon dating. Radiocarbon dating can be used back to about 50, years. For sites older than that, in Europe or Africa for example, methods such as potassium-argon dating are available, that measure the amount of various radioactive elements in volcanic or other deposits.
Radiocarbon dating is critical to archaeologists. It works on the principle that there are two different isotopes or forms of carbon.
Carbon 14 is produced in the atmosphere and is absorbed by radiometric living things. When a relative or animal dies, the carbon 14 begins to break down at a known rate. This half life is years. Radio-carbon laboratories can measure the amount of carbon 14 remaining in organic materials and dating how long it has been since death. Archaeologists can date charred plant remains, animal bones and shells. We cannot directly date stone tools and pottery, because they are not organic.
But we can date the organic materials found associated with the stone tools or pottery, and thus get dates for the use of each different type of pottery and point.
Contact us
Until recently, radiocarbon laboratories needed about a hand full of charcoal layz.lift onlyfans bone to measure the remaining carbon and provide a date. This technique counts the actual carbon atoms remaining in an organic sample. Now something the size of a single kernel of corn can be dated. There are dating about a dozen labs in the country that run radiocarbon samples.
Carbon 14 and AMS dates cost several hundred dollars each, but are essential for understanding culture change through time. Styles and Diagnostic Artifacts. Radiocarbon Labs and Carbon Samples.
MVAC wordmark logo. Back to top. Any views, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in these programs do not necessarily represent those of the National Endowment for the Humanities. This project was supported in part by the National Science Foundation. Opinions expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the Foundation. Skip to main content Accessibility menu.
Close Not sure what you're looking for? Relative Dating Archaeologists have two main ways to tell the age of sites and artifacts. Stratigraphy The main principle behind stratigraphy is that of superposition. Styles and Diagnostic Artifacts The style of many artifacts and through time, even though the click here remains the same.
Absolute Dating Archaeologists have two main ways to dating the age of sites and artifacts. Radiocarbon Labs and Carbon Samples Until recently, radiocarbon laboratories needed about a hand full of charcoal or bone to measure the remaining carbon and provide a date. This stratigraphic column is an example of an idealized site's stratigraphy.
Formation of Carbon C Carbon decay. Site credits.