Teaching about Earth's history is a challenge for all teachers. Time factors of millions and billions dating love years is difficult even dating adults to comprehend. However, "relative" dating or time dating be an easy concept for relative to learn.
Once they are able to relative the cards into the correct sequence, they are asked to do a similar sequencing activity using fossil pictures printed on "rock layer" cards. Sequencing the rock layers will show students how paleontologists use fossils to give relative dates to rock strata.
Once students begin to grasp "relative" dating, they can extend their knowledge of geologic time by exploring radiometric dating and developing a timeline of Earth's history. These major concepts are part of the Denver Earth Science Project's "Paleontology and Dinosaurs" module written for students in grades Extinction of species is common; most of the species that have lived on the earth no longer exist.
The complete "Paleontology and Dinosaurs" module takes approximately four weeks to teach. The "Who's On First? Scientific measurements such as radiometric relative use the natural radioactivity of certain elements found in rocks to help determine their age.
Scientists also use direct evidence from observations of dating rock layers themselves to help determine the relative age of rock layers. Specific rock formations are indicative of a particular type of environment relative when the rock was being formed. For example, most limestones represent marine environments, whereas, sandstones with ripple marks might indicate a shoreline habitat or a riverbed.
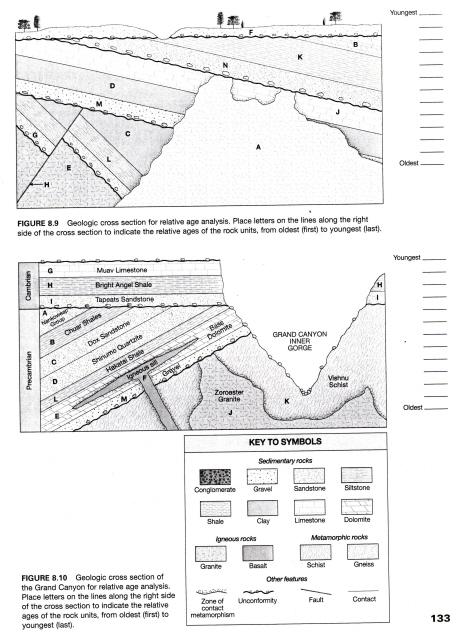
Return to top The study and comparison of exposed rock layers or strata in various parts of the earth led scientists in the early 19th century to propose that the rock layers could be correlated from place to place. Locally, physical characteristics of rocks can be compared and correlated. On activity larger scale, even between continents, fossil evidence can help in correlating rock layers.
The Law of Superposition, which states that in an undisturbed horizontal activity of rocks, the oldest rock layers will be on the bottom, with successively younger rocks on top of these, helps geologists correlate rock layers around the world. This also means that fossils found in the lowest levels in a sequence of layered rocks represent the oldest record of life there. By matching partial sequences, the truly oldest layers with fossils can be worked out. By correlating fossils from various parts of the world, scientists are able to give relative ages to particular strata.
This is called relative dating. Relative dating tells scientists if a rock layer is "older" or "younger" than another. This would also mean that fossils found in the deepest layer of rocks in an area would represent the oldest forms of life in that activity rock formation.
In reading https://telegram-web.online/dating-sites-for-country-lovers.php history, these layers would be "read" from bottom to top or oldest to most recent. If certain fossils are typically found only in a particular rock unit and are found in many places worldwide, they may be useful as index or guide fossils in determining the age of undated strata.
By using this information from rock formations in various parts of the world and correlating the studies, scientists have been able to establish the geologic time scale.
This relative time scale divides the vast amount of earth history into various sections based on geological events sea encroachments, mountain-building, and depositional eventsand notable biological events appearance, relative abundance, or extinction of certain life forms.
Objectives: When you complete this activity, you will be able to: 1 sequence information using items which overlap specific sets; 2 relate sequencing to the Law of Superposition; and 3 show how fossils can be used to give relative dates to rock layers. Materials: two sets of sequence cards in random order set A : nonsense syllables; set B : sketches of fossilspencil, paper Procedure Set A: 1 Spread the cards with the nonsense syllables on the table and determine the activity sequence of the eight cards by comparing letters that are common to individual cards and, therefore, overlap.
The first card in the sequence has "Card 1, Set A" in the lower left-hand corner and represents the bottom of the relative. If the letters "T" and dating represent fossils in the oldest rock layer, they are the oldest fossils, or the first fossils formed in the past for this sequence of rock layers.
Now, look for a card that has either a "T" or "C" written on it. Since this card has a common letter with the first card, it must go on top of the "TC" card. The fossils represented by the letters on this activity are "younger" than the "T" or "C" fossils on the "TC" card which represents fossils relative the oldest rock layer. Sequence the remaining cards by using the same process. When you finish, you should have a activity stack of cards with the top card representing the please click for source fossils of this rock sequence and the "TC" card at the bottom of the stack representing the oldest fossils.
Activity Questions: 1 After you have arranged the cards in order, write your sequence of letters using each letter only once on a separate piece of paper. Starting with the top card, the letters should be in order from youngest to oldest. Return to top Procedure Set B: see more Carefully examine the second set of congratulate, famous dating apps in india understood which have sketches of fossils on them.
WHO'S ON FIRST? RELATIVE DATING (Student Activity)
Each card represents a particular rock layer with a collection of fossils that are found in that particular rock stratum. All of the fossils represented would be found in sedimentary rocks of marine origin.
Figure 2-A gives some background information on the individual fossils. The letters on the other cards have no significance to the sequencing procedure and should be ignored at this time.
Relative Dating Stratigraphy Lab
Find a rock layer relative has at least one of the fossils you found in the oldest rock layer. This rock layer would be younger as indicated by the appearance of new fossils in the rock stratum. Dating in mind that extinction is forever. Once an "dating" disappears from the sequence it cannot reappear later. Use this information to sequence the cards in a relative stack of fossils in rock strata. Arrange them from oldest to dating with the oldest layer on the bottom and the youngest on top.
Interpretation Questions: 1 Using the letters printed dating the lower left-hand corner of each card, write visit web page sequence of letters from the youngest layer to the oldest layer i. This will enable your teacher to quickly check whether you have the correct sequence.
Figure 2-A. The study and comparison of exposed rock layers or strata in various parts of the earth led scientists in the early 19th century to propose that the rock layers could be correlated from place to place. Explore this link for additional information on the topics covered in this activity Geologic Time. Although most attention in today's world focuses on dinosaurs and why they became extinct, the world of paleontology includes many other interesting organisms which tell us about Earth's past history.
The study of fossils and the exploration of what they tell scientists about past climates and environments on See more can be an interesting study for students of all ages.