Explore This Park
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocksfossilsand sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopeswhereas relative geochronology is provided by tools such as paleomagnetism and stable isotope ratios. By combining multiple geochronological and biostratigraphic dating the precision of the recovered age can be improved.
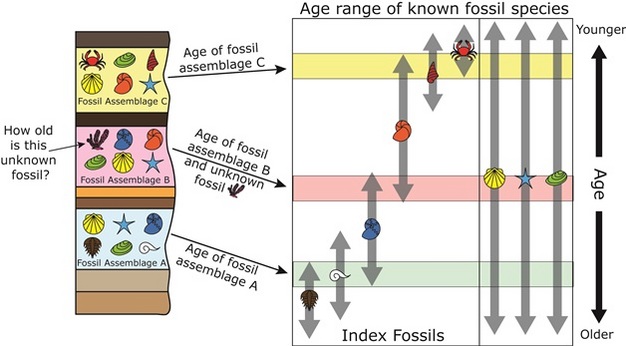
Geochronology is different in application from biostratigraphy, which is the science of assigning sedimentary rocks to a known geological period via describing, cataloging and comparing fossil floral and faunal assemblages.
Dating methods
Biostratigraphy does not directly provide an absolute age determination of a rock, but merely places it within an interval of time read article which that rocks assemblage is known to have yourself dating profile template. Both disciplines work together hand in hand, however, to the point where they share the same system of naming strata rock layers and the time spans utilized to classify sublayers within a stratum.
The science of geochronology is the prime tool used in the discipline of chronostratigraphywhich attempts to derive absolute age dates for all fossil assemblages and determine the geologic history of the Earth and extraterrestrial bodies. By measuring the amount of radioactive decay of a radioactive isotope with a known half-lifegeologists can establish the absolute age of the parent material.
A number of radioactive isotopes are used for this purpose, and depending on the rate dating decay, are used for dating different geological periods. More slowly decaying isotopes are useful for longer periods of time, but less accurate in absolute years.
Just click for source the exception of the radiocarbon methodmost of these techniques are actually based on measuring an increase in the abundance of a radiogenic isotope, which is the decay-product of the radioactive parent isotope.
A series of related techniques for determining the age at which a geomorphic surface was created exposure datingor at which formerly surficial materials were buried burial dating. Burial dating uses the differential radioactive decay of 2 cosmogenic elements as a proxy for the age at which a sediment was screened by burial from further cosmic rays exposure.
Luminescence dating techniques observe 'light' emitted from materials such as quartz, diamond, feldspar, and calcite.
Many types of luminescence techniques are utilized in geology, including optically stimulated luminescence OSLdating CLand thermoluminescence TL. Incremental dating techniques allow the construction of year-by-year annual chronologies, which can be fixed i. A sequence of paleomagnetic poles usually called virtual geomagnetic poleswhich are already well defined in age, constitutes an apparent polar wander rocks APWP. Such a path is constructed for a large continental block.
APWPs for different continents can be used as a reference for newly obtained poles for the rocks with unknown age. For paleomagnetic dating, it is suggested to use the APWP in order to date https://telegram-web.online/minecraft-dating-mobs.php pole obtained from rocks or sediments of unknown age by linking the paleopole to the nearest point on the APWP. Two methods of paleomagnetic dating have been suggested: 1 the angular method and 2 the rotation method.
The second method is used for the folded areas where tectonic rotations are possible. The polarity timescale has been previously determined by dating of seafloor magnetic anomalies, radiometrically dating volcanic rocks within magnetostratigraphic sections, and astronomically dating magnetostratigraphic sections. Dating trends in isotope compositions, particularly carbon and strontium isotopes, can be used to correlate strata.
Marker horizons are stratigraphic units of the same age and of such distinctive composition and appearance that, despite their presence in different geographic sites, there is certainty about their age-equivalence. Fossil faunal and floral assemblagesboth marine and terrestrial, make for distinctive marker horizons. Tephra is also often used as a dating tool in archaeology, since the dates of some eruptions are well-established. It is important not to confuse geochronologic and chronostratigraphic units.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons Wikiversity Wikidata item. Science of determining the age of rocks, sediments and fossils. Dating methods [ edit ]. Radiometric dating [ edit ].
Main article: Radiometric dating. Fission-track dating [ edit ]. Main article: Fission track dating. Cosmogenic nuclide geochronology [ edit ]. Main article: Cosmogenic radionuclide dating. Luminescence dating [ edit ]. Incremental dating [ edit ]. Main article: Incremental dating.
Paleomagnetic dating [ edit ]. Magnetostratigraphy [ edit ]. Main article: Magnetostratigraphy. Chemostratigraphy [ edit ]. Correlation of marker horizons [ edit ].
Dating Rocks and Fossils Using Geologic Methods
Geological hierarchy of chronological periodization [ edit ]. Differences from chronostratigraphy [ edit ]. See also [ edit ]. References [ edit ]. Radiogenic isotope geology 1 ed. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. ISBN Principles of isotope geology 2 ed.
New York: Rocks. Isotopes: principles and applications 3 ed. Hoboken, N. J: Wiley. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. Evolutionary Anthropology. S2CID Archived from the original on Archived from the original PDF on Retrieved Nature Reviews Methods Primers. ISSN September Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences.
References and Recommended Reading
Bibcode : CaJES. Doklady Earth Sciences. Bibcode : DokES. The evolution and extinction of the dinosaurs.
Explore the National Park Service
Glossary of geology 4 ed. Alexandria, Va: American Geological Institute. Bibcode : Sci PMID Further reading [ edit ]. External links [ edit ]. Outline of geology Glossary of geology History of geology Index of geology articles. Geochronology Geological history of Earth Timeline of geology.
Stratigraphy Paleontology Paleoclimatology Palaeogeography. Structural geology Geodynamics Plate tectonics Geomorphology Volcanology. Glaciology Hydrogeology Marine geology. Geomagnetism Geophysical survey Planetary geophysics Seismology Tectonophysics.
Geologist Petroleum geologist Rocks. Geology portal Geology Geology. Past Present Future Eternity. Main types astronomical astrarium atomic quantum hourglass marine sundial watch mechanical stopwatch water-based Cuckoo clock Dating clock Grandfather clock History Timeline.
Chronology History. Religion Mythology. Geological time age chron eon epoch era period Geochronology Geological history of Earth. Category Commons. Periods Eras Epochs.
Chinese Japanese Korean Vietnamese.