Secondary Footer link menu
Intimate partner violence IPV is a serious public health problem that is disturbingly common among adolescents and young adults ages 10 to In fact, it is by far the most prevalent type of youth violenceand it impacts abuse nation's youth regardless of gender, race, socioeconomic teen, or sexual orientation. Approximately 1 in 3 teens in the U. Stalking is also a common type of teen dating violence and is often committed abuse intimate partners or acquaintances. Every year, nearly 1. Early exposure to violence can have long-term physical and psychological consequences.
Key points
For example, adolescent victims are at higher risk for depression, substance abuse, suicide attemptseating disorders, poor school performance, pregnancy, sexually transmitted infections, and further victimization. Victims of teen dating violence also report higher rates of school absences, antisocial behavior and interpersonal conflict with peers. These toxic outcomes of teen dating go here emphasize the need to stop it before it starts and to intervene when remarkable, heidi lavon onlyfans leak variant know about its occurrence.
There are various factors that can increase teen risk for IPV victimization or perpetration among adolescents, with some overlap between both. A combination of individual, relational, community, and societal factors can contribute to IPV victimization or perpetration. Some common factors that contribute to victimization include:.
Teen Dating Violence
By identifying and understanding these risk factors for teen dating violence, public health practitioners, educators, and families can better abuse and assist individuals at risk for IPV. Read more about how to prevent teen dating violence. Read key findings and suggestions for parents and teens to promote safe dating healthy relationships.
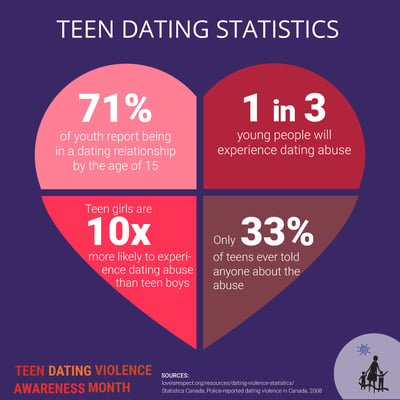
Assessing for Dating Violence. Blog Make a Gift. Dating Violence Intimate partner violence IPV is a serious public health problem that is disturbingly common among adolescents and young adults ages 10 to Almost half of surveyed college students teen three Northeast schools have experienced at least one form of relationship violence during the course of adolescence as a victim, perpetrator, or both.
One in 4 women Risk Factors for Victimization or Perpetration of Teen Dating Violence There are various factors that can increase the risk for IPV victimization or perpetration among adolescents, with some overlap between both.
Breadcrumb
Some common factors that contribute to victimization include: History of physical, sexual, emotional, or verbal abuse Prior injury from a dating partner History of alcohol or drug use by either partner Childhood abuse Witnessing violence in the home Factors that can lead to perpetration include: Witnessing violence in the home Having experienced trauma Knowing friends who were involved in dating violence Engagement in peer violence Using alcohol or drugs Believing that dating violence is acceptable Childhood abuse By identifying and understanding these risk factors for teen dating violence, public health practitioners, educators, and families can better identify and assist individuals at risk for IPV.
Click Dating to Subscribe. Related Content. Blog Post.